Meaning and Types of Stress Positive & Negative
Table of Contents
Meaning of Stress
Stress means a feeling of tension, pressure or anxiety caused by challenging or difficult circumstances. It is natural reaction of our mind and body when we feel that something is out of our control or more difficult than we expect. It occurs when we are nervous, overwhelmed or unable to handle a situation. Like, when you are waiting for your exam results or when there is a strict deadline at work, we may feel tense and under pressure.
Example of Stress
Let’s say your teacher gives you a lot of homework, and you have to finish it by next day. You feel you don’t have enough time, and you start getting stressed and confused about where to start from. This feeling is called stress.
Meaning of Stress Management
Stress management means we learn to control and reduce stress in a healthy and effective way. It involves using techniques and strategies to handle stress so that it doesn’t harm our mind, body, or daily life. If we do not manage stress properly, it can lead to health issues like headaches, fatigue, anger issues or even serious issues like cardiovascular problems. Managing stress helps us stay calm, focused and healthy. It helps us feel in control, stay healthy and tackle life’s challenges without panicking.
Example of Stress Management
Imagine you have three assignments to complete and the deadline is tomorrow. You start feeling anxious and don’t know how to deal with it. To manage your stress, you can do these simple things:
- Breathe deeply: Sit quietly, take a deep breath and exhale slowly. This will help you feel calm.
- Make a plan: Write down which assignments you will complete first, second and third. Doing things step by step makes it easier.
- Take short breaks: After working for 30 minutes, take a 5-minute break to relax. You can stretch or drink water.
- Ask for help: If you’re stuck, ask your parents, friends or teacher to help you.
- Think positively: Instead of worrying about failing, remind yourself, “I can do this.”
- Get good sleep: Don’t stay up too late. Getting a good night’s sleep will help your brain function better.
- Eat healthy: Eat fruit or a light snack to keep up your energy.
By following these steps, you will complete your assignments without much stress and will feel proud of your own self. This is called stress management — finding ways to stay calm and solve problems without getting upset.
Types of Stress
Stress can be divided into two main categories: Positive stress and Negative stress. There are different types of stress under this that affect us in different ways.
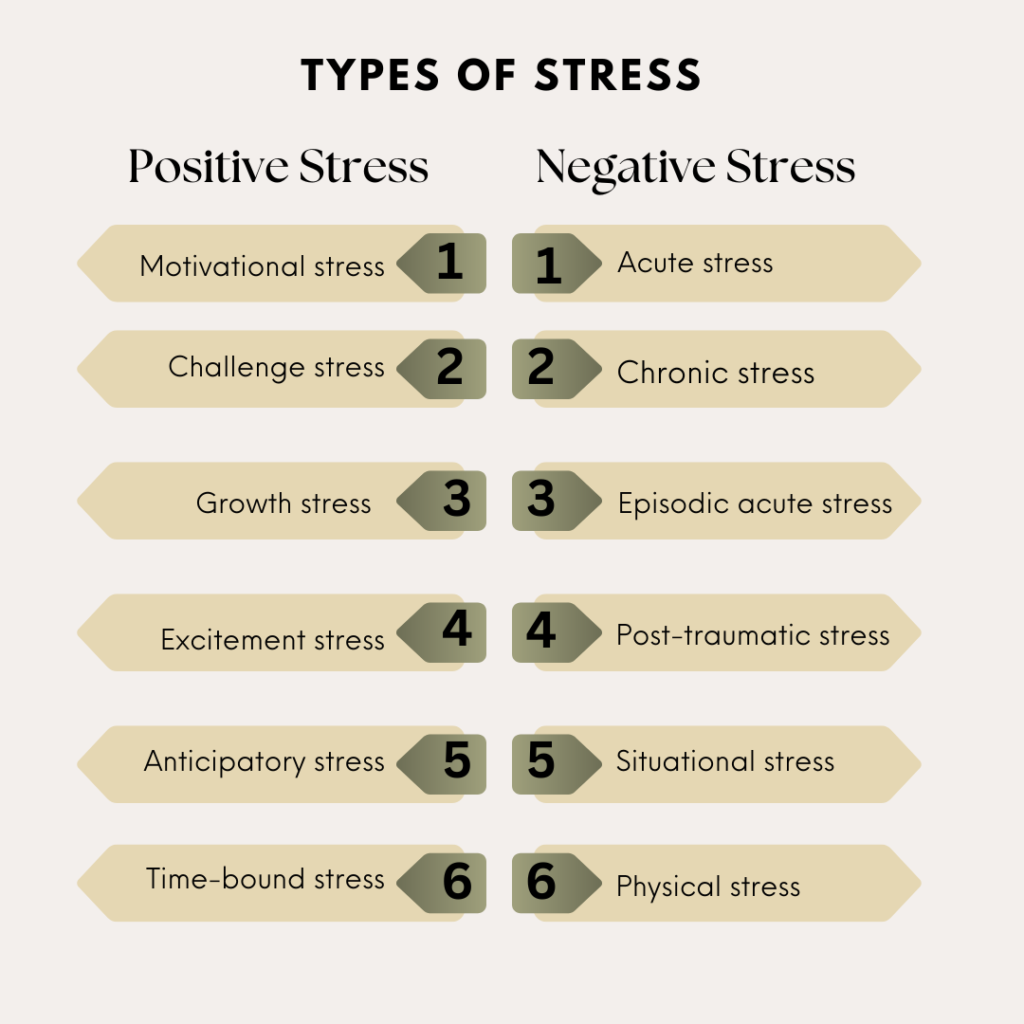
I. Positive stress
Positive stress is the type of stress that makes us feel motivated and excited to take on challenges. It helps us perform better, stay focused, and achieve goals. Positive stress is good for us because it motivates us to do our best.
Types of positive stress
1. Motivational stress
This type of stress gives us the energy to get things done. It makes us feel excited to start something, and helps us stay focused on our goals. All this happen when we have big task or challenge ahead. Motivational stress works when we have a deadline or need to get something important done, motivational stress motivate ourself to work hard and accomplish that goal.
Example: You have a school project that’s due in a few days. The thought of completing it motivates you to study or work on it without delaying.
Before a presentation or exam, you feel nervous, but this nervous energy helps you focus and do your best.
2. Challenge stress
Challenge stress occurs when we face a situation that is difficult but achievable. This kind of stress can excite us because it motivates us to move forward and test our abilities. Challenge stress works when we feel we can handle it, even though the challenge is difficult. This kind of stress is helpful because it motivates us to work hard to succeed.
Example: Suppose you start a new job where they want you to learn new skills because tasks are difficult, but you are excited to improve and do well.
When you are participating in a competition, such as a race or contest, where you feel challenged but you are also excited to give your best.
3. Growth stress
Growth stress occurs when we step out of our comfort zone to try to grow and become better. It can be stressful because it involves doing things that we’ve never done before or taking on new responsibilities. Growth stress works when it helps us move forward in life, whether personally or professionally. It can make us feel anxious, but it also helps us learn and develop new skills.
Example: When you decide to learn a new language. At first it seems daunting and overwhelming, but the stress of learning motivates you to study and move forward.
When you move to a new city for a job or school. It’s stressful because everything is new, but it’s also exciting because you’ll learn and experience new things.
4. Excitement stress
Excitement stress comes from the excitement of doing something fun or thrilling. It’s not bad stress because it makes us feel alive and ready to enjoy life. Excitement stress works when we’re looking forward to an event or activity. It makes us feel energetic and ready to immerse ourself in the experience.
Example: When you’re preparing for your birthday party or wedding. You feel excited because it’s a fun event, but preparing and planning also causes stress.
You’re going on vacation to a new place, and the idea of exploring new places makes you feel excited and energetic.
5. Anticipatory stress
Anticipatory stress is when we feel excited and little nervous about thing of future. This type of stress occurs when we are really excited about the event we were waiting for. Anticipatory stress works when we know something exciting is about to happen, we start to feel stressed in a positive way. This can motivate us to prepare or plan for the upcoming event.
Example: You are waiting for a big event, such as a concert or a vacation, and you feel excited about it. Thinking about it makes you feel energetic and hopeful.
You are waiting to meet a friend after a long time and the anticipation creates excitement and a little stress when you think about the reunion.
6. Time-bound stress
Time-bound stress occurs when we have a deadline to complete a particular task. This type of stress motivates us to work efficiently and manage our time wisely. It helps us stay focused, organized, and determined to complete our work on time.
Example: Suppose you have to submit a project in 2 days. Deadline pressure motivates you to plan and work efficiently to complete it on time.
When you study the night before an exam it gives you stress but it will also motivate you and help you to revise quickly at your best.
II. Negative Stress
Negative stress, or distress, is a type of stress that makes us feel overwhelmed, anxious or unable to cope with situations. It often affects our physical and mental health, reduces productivity and harms our relationships because we get too much irritated.
Types of Negative Stress
1. Acute stress
Acute stress is short-term stress that occurs suddenly due to a specific event or situation. It can make us feel anxious, upset or unable to think clearly. Acute comes to us quickly, but it also goes away when the situation is over. However, it makes us feel tired or shaken for a while.
Example: You suddenly have a fight with a friend or family member.
You narrowly avoid an accident while driving, causing your heart to beat faster and hands to shake.
2. Chronic stress
Chronic stress is long-term stress that lasts for weeks, months, or even years. It happens when we’re constantly in stressful situations and can’t find a way to resolve them. Chronic stress harm our health. Chronic stress increases over time and becomes part of our daily life, without even we realizing it. This stress can lead to serious illnesses like headaches, sleep problems, and even heart disease.
Examples: Dealing with financial problems for a long time.
Living in a toxic work environment where you feel stressed every day.
3. Episodic acute stress
Episodic acute stress happens when someone repeatedly experiences acute stress. People who experience episodic acute stress often feel like they’re always in crisis or unable to meet their responsibilities. Episodic acute stress happens when we over burden ourself with too much of work, don’t manage time well or are constantly worrying about things. This makes us feel anxious, irritable and tired.
Example: A student who is always stressed of every test or assignment deadline because they wait for the last minute to do it.
A person who constantly feels overwhelmed with work and doesn’t have time to relax.
4. Post-traumatic stress
Post-traumatic stress occurs after experiencing a very shocking or life-threatening event, such as an accident, natural disaster or violence. It can cause fear, anxiety and long-term emotional pain. Traumatic stress can lead to conditions such as PTSD (post-traumatic stress disorder), where a person keeps on reliving the traumatic event. This affects their emotions and daily life.
Examples: Person who survives a car accident and now afraid to drive again.
Person who witnessed a natural disaster and having nightmares at night.
5. Situational stress
Situational stress occurs when we are in a situation that makes us feel anxious, confused or helpless. It is usually temporary but get panic or frustrated at the time. Situational stress occurs when we are unprepared or feel anxious of an unexpected event.
Example: Suddenly when you are asked to give an impromptu speech in front of a crowd, and you become nervous or anxious.
When you are already running late for an important function and get stuck in a traffic.
6. Physical stress
Physical stress occurs when your body is under pressure due to illness, injury or lack of rest. It can also be caused by unhealthy habits such as poor diet, lack of sleep or workload. Physical stress makes our body weak and can cause exhaustion, muscle pain or other health problems.
Examples: Working long hours without enough rest, makes you feel tired.
Not eating properly or not getting enough sleep, makes you feel weak and irritable.
FAQ About Stress in Organizational Behavior:
What is stress?
Is stress always bad?
What is Positive stress?
Different types of positive stress?
Challenge stress: Occurs when we face a difficult but achievable challenge, such as participating in a competition.
Growth stress: Occurs when we step out of our comfort zone, such as learning a new skill.
Excitement stress: Comes from thrilling or fun activities, such as planning a vacation or birthday party.
Anticipatory stress: Occurs when we feel excited and nervous about a future event, such as waiting for a reunion.
Time-bound stress: Occurs when we have a deadline to complete a particular task.
What is negative stress?
Different types of negative stress?
Chronic stress: Long-term stress that lasts for months or years, such as financial problems or a toxic workplace.
Episodic acute stress: Repeated experiences of acute stress, often due to poor time management or persistent worries.
Post-traumatic stress: Caused by life-threatening or shocking events, such as an accident or disaster.
Situational stress: Temporary stress caused by unexpected situations, such as a speech given suddenly.
Physical stress: Resulting from physical problems, such as illness, injury, lack of sleep, or poor diet.
Difference between acute stress and chronic stress?
Chronic stress: Long-term stress that lasts for weeks, months or years, such as ongoing financial problems or a stressful job.
Why is stress management important?
What are simple ways to reduce stress?
Exercise regularly to relieve stress.
Maintain a healthy sleep schedule.
Break tasks down into smaller steps and set priorities.
Take time to relax by doing things you enjoy, such as reading etc.
How can deep breathing help manage stress?
Conclusion of Stress in Organizational Behavior:
Stress affects everyone in different ways, but stress isn’t always bad. Positive stress helps us achieve goals, focus, and make us stronger. Negative stress, on the other hand, can make us feel anxious, tired, and unwell. Knowing the types of stress and the impact can help us manage it better. When we learn to handle stress in a healthy way, we can live a happier, healthier, and more balanced life.







Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/cs/join?ref=S5H7X3LP
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.